How to visualize your brainstorming sessions for max results
“The idea is the most expensive item in the world.” These words by Steve Jobs nail the essence of mentorship and business growth in the best way possible.
Indeed, the ability to find creative solutions to business problems separates professionals from mediocre entrepreneurs. Mentors have mastered the art of stellar brainstorming to help others set growth goals, and that’s why we ask them for help when willing to validate our ideas before executing or when we seem stuck.
In this article, we’ll reveal the nature of brainstorming for business idea generation and share the 7-10-13 strategy some mentors use to make the most out of it.
Why 7-10-13? Keep on reading to get it.
7 rules for efficient brainstorming sessions
First, the basics:
What is brainstorming?
Brainstorming is the idea generation process of taking every thought — even the most awkward and seemingly irrelevant — into consideration.
Some of those ideas will go through a compare and contrast process to transform into business and marketing decisions later. But the primary goal of brainstorming is to awaken your subconscious thinking genius and make it go above the well-known ordinary concepts and perceived “best practices.”
A brainstorming session can be individual or group. Professional mentors may consider the former more effective as they are experienced enough to organize the process. For business owners and marketers working in teams, group brainstorming will work better:
It allows every team member to get involved in business growth, become more proactive, and develop critical thinking for more effective business solutions.
To make the most out of your group brainstorming session, follow the next seven rules:
- Organize a workspace. A room with corresponding tools and atmosphere activates a thinking process and motivates one to generate creative ideas. Everything matters: walls color, light, comfortable chairs, and devices; they empower productivity and desire to work.
- Choose one person who’ll be a secretary for your session: They’ll write down ideas on a flip chart.
- Organize a warm-up: If your brainstorming session includes people from different departments who didn’t work as one team before, do your best to introduce them to each other and share some insights on the project to set a friendly atmosphere.
- Set a goal: Even if you think they know what you are doing here, describe the purpose of the brainstorming session before you start.
- Encourage every person in your brainstorming group to speak.
- Give some time: Don’t push and allow the team to organize thoughts.
- Brainstorm in small groups: Don’t gather more than ten people for one session.
10 mistakes to avoid during a brainstorming session
Below are ten mistakes some managers make when organizing a brainstorming session. They make it less effective and prevent group members from unleashing their creativity to the max.
- No specific topic. Avoid something a la, “Now give me all ideas that come to your mind!” Instead, ask a particular question or assign a theme for your team to hook up with and start a process.
- Motivation lack. If your team isn’t proactive and motivated enough to grow your business and create something remarkable, brainstorming won’t bring any results.
- No problem-solving skills. They are critical for you and your team to succeed with brainstorming and choosing the most actionable ideas from those brainstormed.
- Same-thinking team members. What’s the point of a brainstorming session with ten marketers with similar mindsets? The scope of their competence will limit their creativity. Instead, invite specialists from different departments to your session: a copywriter, a designer, a custom service officer, etc.
- Too many coffee breaks. They are critical to clearing heads and refreshing minds, but they won’t work if you organize them every half an hour. People just won’t have time to engage in the thought process!
- Ignoring out-of-the-box solutions. During brainstorming, every idea matters. You’ll have time to validate it after consulting with a mentor.
- Rush. Don’t cry for ideas here and now; give your brainstorming team enough time to think.
- Competition. Don’t invite people from competitive departments to a brainstorming session; it will influence their ideas and decisions as they might not stay unbiased.
- Why so serious? Humor and jokes can help people relax and not be afraid of communicating unusual or seemingly irrelevant ideas. Some of them may appear as creative business solutions later.
- Immediate approvement. Don’t hurry up to approve all the ideas from those brainstormed during a session. Write down now, analyze and validate later.
13 visual techniques for generating stellar business ideas
And now, to practice:
Are there any particular brainstorming techniques to use during a session for generating as many working business ideas as possible? Below are 13 you can try; all are visual for a clearer understanding, idea connection, and application.
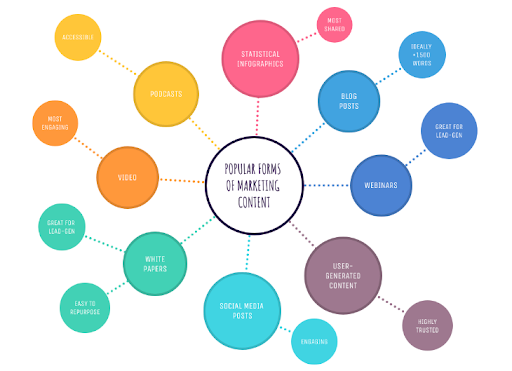
1 — Mind Maps
Mind maps organize information and visualize the relationships between the ideas you generate during brainstorming. They also help break down concepts and analyze them.
Write down the topic in a map’s center and add branches to connect all the sub-ideas. Like this:
2 — Brains Switch
Ask the members of your brainstorming session to write their ideas and questions on paper. Then, they exchange writings and come up with alternative ideas related to those they’ve got from colleagues.
Thus, you break a traditional in-order chain of thinking, encouraging the brain to work differently.
3 — Brainwriting
This technique is perfect for brainstorming teams with shy or introverted members or those with no speaking skills. Instead of speaking out about their ideas, people write them down.
It helps everyone get engaged in the session, be productive, and generate more ideas: The technique works like freewriting, where you just follow the train of thoughts and allow them to appear on paper with no prescribed structure.
4 — Mood Boards
A mood board looks like a collage, collecting images and texts to convey a project for better visualization. You can use it to conceptualize a brainstorming session with color palettes, textures, typography, etc.
It’s a great way to unleash creativity and stimulate idea generation.
5 — Topic Clusters
A topic cluster looks like a diagram that sketches ideas and identifies connections. It allows you to structure the process of idea generation:
Pick a topic to explore, place it in the center, and decide on several related subtopics. For example, if you take sports, subtopics can be football, tennis, hockey, etc. Now it’s time to brainstorm subtopics for football, tennis… Well, you’ve got the point.
Thus, you build a chain of related ideas. The technique is super cool when you need to generate content ideas for your business blog, social media accounts, and other marketing channels.
6 — SCAMPER
SCAMPER goes for looking at one idea from seven different angles:
What to substitute in your product/service to make it better; what ideas or resources to combine for a more efficient output; what to adapt, modify, put to another use, eliminate, and rearrange to achieve the desired result.
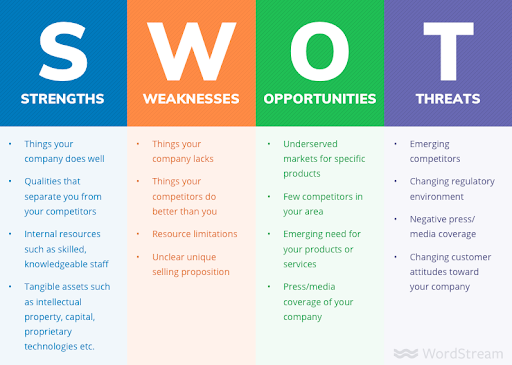
7 — SWOT
Marketers and business owners know the concept of SWOT for ideas generation and approvement:
You draw a four-part table, identifying the following criteria for your idea:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
It helps to understand where you are, plan, and focus on the steps to take or avoid for positive results.
8 — Six Thinking Hats
Six thinking hats are a technique for providing direction to group thinking. You take six thinking styles with one color for each, allowing the team to look at ideas from different perspectives.
A white hat is for facts, a red one — feelings, and a black one is for cautions (judgment and morality). Yellow represents benefits, a green one is for creativity (new ideas, opportunities), while a blue hat serves for a process (next steps, conclusions, action plans).
9 — Six-Pointed Star
Each point of the star is for a question to ask about the idea you discuss at the brainstorming session. It’s also known as the 5W+1H technique: Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How.
First, your team generates at least three questions for each point. And then, you all discuss answers to each question to find solutions. It helps to build a clear vision of the steps you’ll need to take.
10 — Lotus
A lotus diagram helps visualize smaller components of big ideas for easier analysis and prioritization.
Start with the main topic and expand it with subtopics and solutions or related themes for each one. The difference between lotus diagrams and mind maps or topic clusters lies in the visualization type:
Mind maps look like trees; a topic cluster reminds a spider; lotus diagrams are like flowers: the more ideas you generate, the more petals they’ll have.
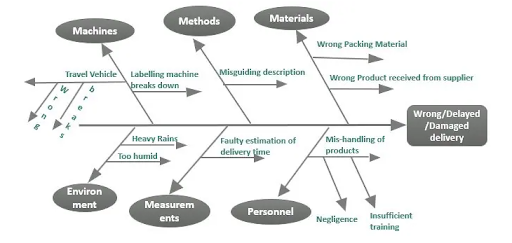
11 — Fishbone
Consider a fishbone diagram when facilitating a reverse brainstorming session. What does it mean?
Instead of finding ideas and solutions to a problem, your team generates its causes. Also known as a cause and effect diagram, fishbone helps you analyze business situations and deliver business plans.
- A problem will be the head of your fish.
- A team will generate ideas on how to cause this problem or make it even worse.
- Write down core causes as fishbones and reverse solutions — as ribs.
12 — Concept Maps
This visual technique is for identifying the relationships between ideas and concepts. It helps to structure everything that comes to your mind during brainstorming and make connections for further implementation.
So, identify a topic and encourage your team to write down all the ideas and associations that come to mind when they think about it. After that, draw a map to connect all related facts/themes, etc.
13 — Flowcharts
A flowchart will work for brainstorming sessions where you try to identify business goals and reveal the steps to take to achieve them.
It’s a map helping you find the way from point A (your current situation) to point B (goals), with the steps you need to take for that in between. Your brainstorming team generates the ideas on these steps, aligning them one by one to complete the process.
Over to you
Now that you know the nature of brainstorming and its role in business success, it’s time to try it. Organize a brainstorming session, invite team members to join you, and choose a technique from the above 13 that fits your project best.
Once finished, analyze all the ideas for validity or consult with a mentor who’ll help you grow.